Cognitive and brain improvement are decided by dynamic interactions between genes and setting throughout the lifespan.
Aside from marker-by-marker analyses of polymorphisms, biologically significant options of the entire genome (derived from the mixed impact of particular person markers) have been postulated to tell on human phenotypes together with cognitive traits and their underlying organic substrate.
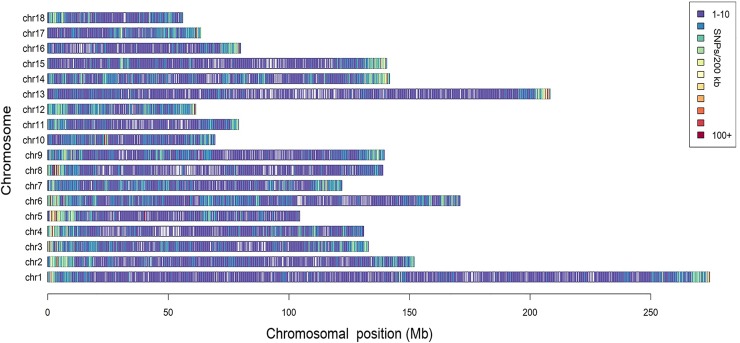
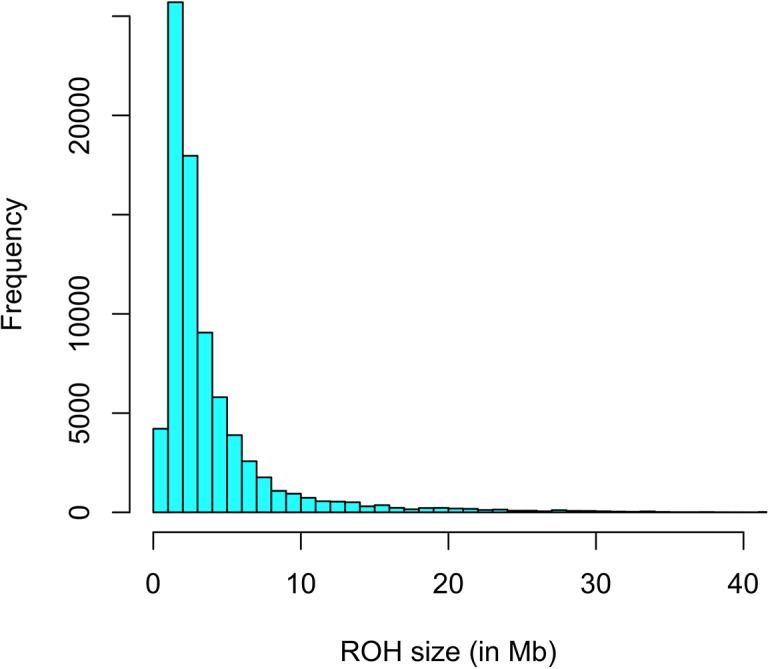
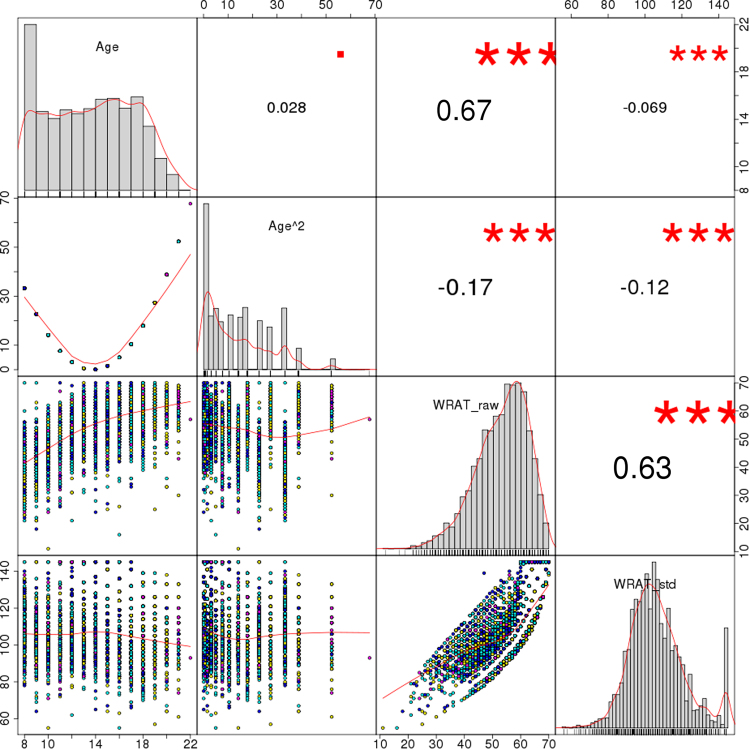
Here, estimates of inbreeding and genetic susceptibility for schizophrenia calculated from genome-wide data-runs of homozygosity (ROH) and schizophrenia polygenic risk rating (PGRS)-are analyzed in relation to cognitive talents (n = 4183) and brain construction (n = 516) in a general-population pattern of European-ancestry contributors aged 8-22, from the Philadelphia Neurodevelopmental Cohort. The findings counsel {that a} increased ROH burden and increased schizophrenia PGRS are related to increased intelligence.
Cognition-ROH and cognition-PGRS associations obtained on this cohort could, respectively, proof that assortative mating influences intelligence, and that people with excessive schizophrenia genetic risk who don’t transition to illness standing are cognitively resilient.
Neuroanatomical knowledge confirmed that the consequences of schizophrenia PGRS on cognition could possibly be modulated by brain construction, though bigger imaging datasets are wanted to precisely disentangle the underlying neural mechanisms linking IQ with each inbreeding and the genetic burden for schizophrenia.

Research Techniques Made Simple: Genome-Wide Homozygosity/Autozygosity Mapping Is a Powerful Tool for Identifying Candidate Genes in Autosomal Recessive Genetic Diseases.
Homozygosity mapping (HM), often known as autozygosity mapping, was initially used to map genes underlying homozygous autosomal recessive Mendelian illnesses in sufferers from intently genetically associated populations, adopted by Sanger sequencing.
With the rise in use of next-generation sequencing approaches, comparable to whole-exome sequencing and whole-genome sequencing, along with superior bioinformatics filtering approaches, HM is once more rising as a strong methodology for the identification of genes concerned in illness etiology.
In addition to its usefulness for analysis, HM is efficient in scientific genetic providers, rising the effectivity of molecular diagnostics. For autosomal recessive Mendelian issues with intensive genetic heterogeneity, HM can scale back each value and turnaround time of mutation detection within the context of next-generation sequencing and can obviate costly screening, comparable to biochemical testing within the setting of metabolic genodermatoses or antigen mapping for epidermolysis bullosa.
It is subsequently essential for dermatology clinicians and researchers to know the processes, principal makes use of, and benefits and limitations of HM when ordering or performing genetic checks for sufferers affected by heritable pores and skin issues.